In industries like manufacturing, metallurgy, and aerospace, understanding material hardness is critical for determining the durability, wear resistance, and performance of various materials. Two of the most widely used hardness tests are the Vickers hardness test and the Rockwell hardness test.
However, these tests measure hardness differently, which often leads to the need for conversion between the two scales. This guide will explore the Vickers to Rockwell hardness conversion process, provide detailed information on both hardness scales, and offer a conversion table for easy reference.
Introduction to Vickers and Rockwell Hardness Tests
Material hardness testing is a vital process that assesses a material's resistance to deformation. Both the Vickers and Rockwell hardness tests provide reliable measurements, but they use different methods to arrive at their respective hardness values:
1. Vickers Hardness Test
This method uses a diamond pyramid indenter with a square base. The indenter is pressed into the material with a specific load, and the size of the indentation is used to calculate the hardness value (HV). The Vickers test is highly versatile and can measure both very soft and very hard materials with extreme precision.
2. Rockwell Hardness Test
The Rockwell test measures hardness by assessing the depth of indentation created by an indenter (either a diamond cone or a steel ball) under a specific load. It is widely used in manufacturing due to its speed and efficiency, with different scales (e.g., Rockwell B, Rockwell C) for various materials.
While both methods are effective, situations often arise where it's necessary to convert between Vickers and Rockwell hardness values, particularly when dealing with international clients or cross-industry standards.
Explore our range of Vickers hardness testers and Rockwell hardness testers to ensure you have the right tools for precise material testing.
The Importance of Converting Vickers to Rockwell

Converting Vickers hardness to Rockwell hardness is a common need, especially when different industries or clients use specific standards. Some of the reasons you may need to convert between these two hardness scales include:
1. Meeting Client Specifications
Different clients may require material hardness values in a specific scale. For example, a manufacturer might test materials using the Vickers scale but need to report the hardness values in Rockwell C for a client’s requirements.
2. Compliance with International Standards
Different regions and industries may adopt different hardness scales. For instance, some international standards prefer the Rockwell scale, while others may use Vickers.
3. Comparison Across Industries
When working with suppliers or clients from various industries, it’s important to convert between hardness scales to ensure material compatibility and performance.
For versatile hardness testing equipment that covers multiple scales, take a look at our universal hardness testers, capable of performing tests across both Vickers and Rockwell scales.
How to Convert Vickers Hardness to Rockwell Hardness
Converting Vickers hardness to Rockwell hardness involves using standardized conversion charts or formulas. These conversions are based on empirical data collected from testing various materials and comparing the results of different hardness tests. The relationship between the two scales depends on the material and its hardness range.
Here’s a simplified process for converting Vickers hardness (HV) to Rockwell hardness (HR):
1. Obtain the Vickers Hardness Value (HV): Conduct a Vickers hardness test on the material using the appropriate indenter and load for your material.
2. Consult a Conversion Chart: Use a conversion chart to find the equivalent Rockwell hardness value for the material. Different Rockwell scales (such as Rockwell B or C) may apply depending on the material and its hardness range.
3. Factor in Material Type: Some conversions may vary depending on the material type, as different metals respond differently to the Vickers and Rockwell testing methods.
Below is a sample conversion table, referencing values from ASTM E140 and other standardized conversion resources.
Vickers to Rockwell Conversion Table
This table provides a quick reference for converting Vickers hardness values to approximate Rockwell C and Rockwell B hardness values. Keep in mind that these values are approximations and may vary slightly depending on the material being tested.

Download Vickers Hardness to Rockwell C PDF Conversion Chart
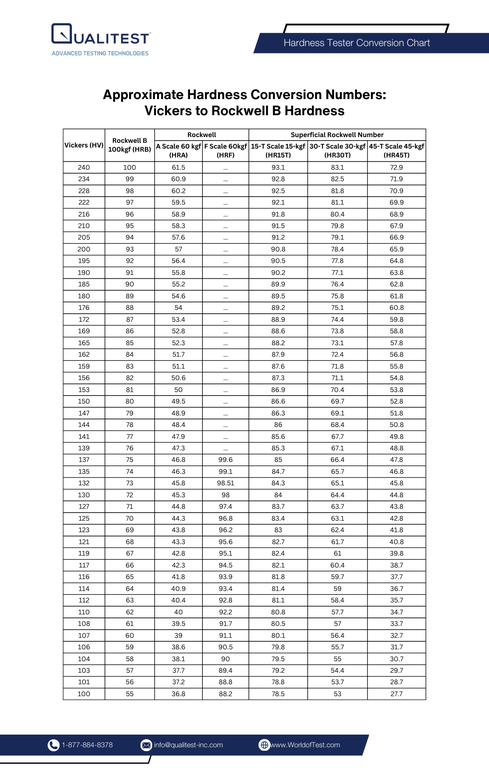
Download Vickers Hardness to Rockwell B PDF Conversion Chart
This table can serve as a handy guide, but for high-precision applications, always refer to more detailed charts or conversion software that factors in the specific material type and its characteristics.
Applications of Vickers to Rockwell Conversion
Converting between hardness scales is a common requirement in industries that involve material testing, manufacturing, and quality assurance. Some key industries where Vickers to Rockwell conversion is frequently needed include:
1. Automotive Industry: Automotive components must meet specific hardness requirements to ensure durability and resistance to wear. Converting hardness values between Vickers and Rockwell scales ensures that components meet these industry standards.
2. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry often requires high-precision testing of metals and alloys. Vickers hardness testing is frequently used, but Rockwell hardness values may be needed for specific client requirements or material certifications.
3. Metallurgy and Material Science: Researchers working on developing new materials, especially alloys, often need to convert between hardness scales to compare the performance of different materials under various conditions.
By converting between scales, industries can ensure that materials meet their specific use-case requirements and performance expectations, regardless of the testing method used.
Understanding conversion of vickers hardness to rockwell hardness is important for material testing across multiple industries. Whether you're working in manufacturing, aerospace, or quality control, using accurate conversion tables ensures that your materials meet the necessary specifications. By having the right tools and resources, you can confidently convert between these two scales and ensure that your materials are tested and reported correctly.
For professional testing equipment that supports both Vickers and Rockwell scales, explore our range of hardness testers, including Vickers hardness testers and Rockwell hardness testers.